Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN): Benefits, Side Effects & Dosage
- Introduction
- Potential Benefits of NMN
- Recommended Dose for Human Consumption
- Side Effects of NMN Supplementation
- Active NMN Clinical Trials
- Future NMN Research
Thanks to advances in modern medicine, individuals around the world have been living longer. In addition to lower mortality and increased survival, a sustained drop in fertility has shifted the proportion of older individuals upwards. According to the World Health Organization, the world’s population of older individuals is expected to reach 2.1 billion by 2050, doubling the aged population.
A longer life, however, does not guarantee a healthy life. As we age, our organs accumulate damage and progressively decline, making us susceptible to diseases. This is why many scientists have shifted their attention towards finding ways to slowdown, prevent, or even reverse aging. If successful, so-called anti-aging therapies could reduce the prevalence of age-related disease and help us live longer and healthier lives.
Currently, one of the most promising anti-aging targets under study is a vital molecule called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). NAD+ mediates the production of the energy our cells need to function and survive, fueling enzymes key in repairing DNA damage. As we age, this indispensable molecule progressively declines.
Many scientists hypothesize that the age-related decline in NAD+ underlies the organ decline that characterizes aging. It follows that, by restoring NAD+, our cells become healthier, our organs become healthier, and we become healthier. If this can be achieved, a lack of high-mortality age-related diseases like cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer will allow us to live longer.
How can we restore our NAD+ levels? Since NAD+ occurs naturally, our cells have the machinery necessary to make it on their own; they just need the necessary biochemical components. Our cells generate molecules like a factory assembly line where each component is the precursor for the next. The biochemical precursor to NAD+ is called nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Unlike NAD+ itself, NMN can be ingested orally and can thus be taken in supplement form to raise NAD+ levels.
Potential Benefits of NMN
NMN feeds into the production of NAD+, providing our cells with the energy needed to function. There are several factors thought to underly the aging process, a lack of cellular energy being one of them. Genetic instability resulting from DNA damage is also one of these factors. NAD+ plays a key role in activating enzymes that maintain DNA integrity, thus promoting genetic stability. Given its central role in these cellular processes, the potential benefits of boosting NAD+ with NMN extend to nearly all body systems. Below are some of the better-known examples.
Improves Brain Function
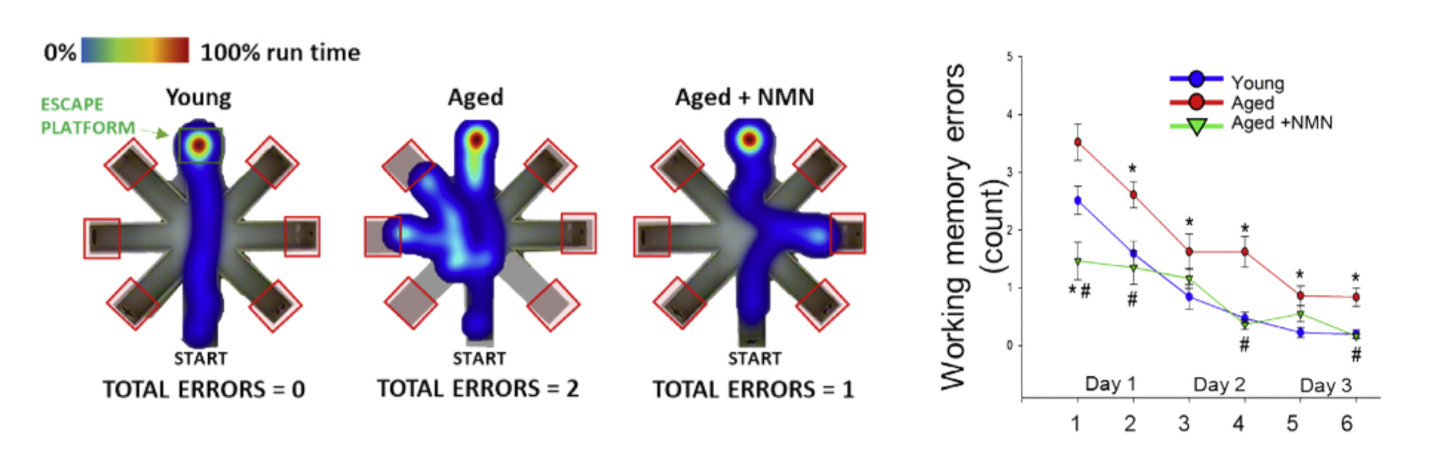
Perhaps one of the most devastating age-related diseases is Alzheimer’s disease, whereby the afflicted are robbed of their memories. NMN has been shown to improve cognition in rodents with Alzheimer’s and reduce brain plaques and neurodegenration in Alzheimer’s mice. While Alzheimer’s is an end-stage disease, many older adults also suffer from cognitive impairments — inability to learn, remember, and think properly. These age-related cognitive impairments have been prevented by NMN in mice. Cognitive impairments are sometimes associated with depression, which has also been shown to be alleviated by NMN in mice.
Because our blood vessels become dysfunctional as we age, blood flow to our brain becomes impaired, leading to cognitive impairments. NMN has been shown to increases blood flow to the brain and improve cognitive function in mice. When the blood vessels in our brain become clogged, we can have a stroke, whereby our brain tissue becomes damaged. NMN has been shown not only delay stroke onset, but also to prevent stroke damage, and improve cognition and mitochondrial health after stroke in rodents.
Restores Blood Vessel Health
Our blood vessels transport vital nutrients to each of our cells. As we age, our blood vessels become rigid and more susceptible to blockage, which can lead to heart attack or stroke. NMN has been shown to reverse vascular aging by restoring blood vessel elasticity in mice. Senescent cells — growth arrested cells that accumulate with aging — contribute to the aging of many organ systems, including the vascular system. In mice, NMN stops blood vessel aging my reducing senescent cells, leading to alleviation of hypertension. One of the ways senescent cells contribute to aging is by promoting inflammation, which underlies nearly every age-related disease. NMN has been shown to reverse blood vessel dysfunction by reducing blood vessel inflammation in mice.
Improves Muscle Function
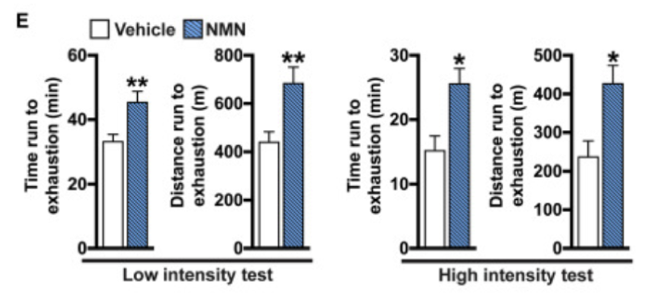
We rely on our skeletal muscles for movement, stability, and strength. As we age, our muscles lose their ability to regenerate and grow, leading to the age-related decline in muscle strength and size called sarcopenia. Along with muscle weakness, we also become more fatigued and have less physical endurance. NMN seems to reverse these conditions, as one of its transporters has been shown to increase strength and physical endurance in mice. Furthermore, NMN improves muscle strength and performance in older men, and enhances oxygen utilization and exercise endurance in middle-aged runners. On the other hand, another NAD+ precursor called nicotinamide riboside (NR) does seem to improve muscle function.
Promotes Healthy Heart
Our heart can barley afford to skip a beat before death ensues, leaving little room to wonder why heart disease is the worldwide leading cause of death.
As we age, our heart becomes more susceptible to irregular beats, which have devastating outcomes, such as heart failure. NMN has been shown to protect against heart failure in mice. Our heart tissue is precious, as it is not known to regenerate. Instead, damaged tissue manifest in scarring (fibrosis), leading to heart dysfunction. NMN recovers mouse heart function by reducing scarring. Beating constantly and evermore, the heart requires large quantities of energy. For this, it needs healthy mitochondria. NMN improves heart metabolism and protects against heart failure, in part by rejuvenating mitochondria.
Our heart is part of the cardiovascular system, pumping oxygen-containing blood to the rest of our organs. When the blood vessels surrounding our heart become clogged, the adjacent tissue becomes damaged and dies due to a lack of oxygen. This is called ischemia and commonly leads to heart attacks. In mice, NMN protects the heart from ischemic injury. This protection is synergistically improved with stem cell therapy and melatonin. Enhances Cancer Suppression
Aids in Cancer Therapy
One of the most new and promising therapies against cancer are called immunotherapies. These therapies utilize immune cells to suppress tumor growth. Immunotherapies have not been perfect, but in rodents NMN has been shown to enhance the tumor killing capabilities of several different types, including natural killer cell therapy, CAR-T cell therapy, and PD-1 mediated therapy.
While immunotherapies may be a cancer therapy of the near future, chemotherapies are still used widely but come with many harmful side effects. NMN has been shown to reduce these unwanted side effects, such as heart tissue damage and cognitive impairments in mice.
Protects Against Obesity and Diabetes
Obesity is linked to a wide array of metabolic deficiencies, including insulin resistance — when are cells cannot utilize glucose due to impaired insulin signaling — which can lead to diabetes. Mitochondria are the final cellular destination for the food we eat to be converted into energy, making them of key importance in metabolism and related diseases. NMN has been shown to double the amount mitochondria in the livers of obese mice, which could protect against obesity. Stimulating fat breakdown with NMN could also help obese individuals lose fat. Furthermore, NMN improves the metabolism and health of mice born to obese mothers.
Eating too much and becoming obese wreaks havoc on our metabolism and can lead to diabetes. Aging makes both of these conditions worse. In mice, NMN has been shown to reverse diet and aged induced diabetes and prevent the kidney disease and neuron degeneration associated with diabetes, suggesting that NMN can protect against these metabolic impairments. To support this, NMN has been shown to improve muscle insulin sensitivity in older women. Thus, While lifestyle adjustments like consistent exercise and a healthy diet are of paramount importance, NMN may protect against obesity and diabetes.
Could Treat Eye Aging and Injury
Macular degeneration is an age-related disease involving the degeneration of a region of the retina that allows us to see clearly. Thus, more severe forms of macular degeneration can cause blindness. NMN has been shown to repair the mitochondrial dysfunction associated with macular degeneration in mice.
As we age, our eyes become dry and inflamed. NMN has been shown to reduce inflammation and increase oil secretion, treating dry eye in mice. NMN has also been shown to reduce cell death and wound size after eye injury.
Promotes Organ Health
In addition to slowing down aspects of the aging brain, vasculature, muscle, heart, metabolism, and eye, NMN has also been shown to rejuvenate bone stem cells and promote bone formation in rodents. It also reverses intestinal aging, protects against age-related kidney deterioration, and inhibits the onset of liver fibrosis in rodents. Thus, NMN also slow aspects of aging bone, intestines, kidney and liver.
Revitalizes Reproduction
With age comes fertility problems, especially with women. This stems from problems with oocyte (egg) quality. NMN has been shown to improve the age-related decline in oocyte quality and number, as well as female fertility in mice. NMN also protects oocytes from toxins in pigs.
Enhances Maintenance of DNA Repair
Our DNA codes for the building blocks of our cells but accumulates damage as we age. Repairing DNA damage can prevent age-related diseases. NAD+ fuels enzymes called sirtuins — sometimes thought of as the guardians of our healthspan. Sirtuins play a key role in repairing DNA.
Also, each time our cells divide, the DNA at the ends of our chromosomes (telomeres) grows shorter. At a certain point, this telomere shortening begins to damage our genes and cells. Sirtuins slow this process by stabilizing telomere length.
Since sirtuins rely upon NAD+ to function, there has been an effort to enhance sirtuin activity through NAD+ boosting methods. Along these lines, studies have demonstrated that feeding mice NMN activates sirtuins. NMN also repairs DNA damage resulting from radiation and old age in mice. Furthermore, in both mice and humans, NMN increases telomere length.
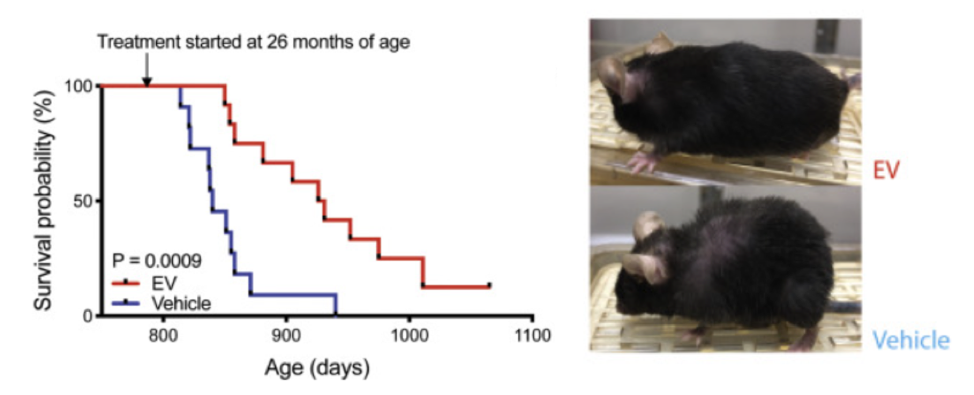
NMN studies from institutes like Harvard University and Washington University have shown that supplementing with the molecule or enhancing NMN synthesis promotes longevity and health during aging in rodents. Sinclair and colleagues found that when aged mice drank NMN-infused water, their running endurance almost doubled. Further studies have demonstrated that injecting mice with NMN preserves cognition during aging. Moreover, a study from Imai and colleagues indicates that an upsurge in NMN synthesis more than doubles the remaining lifespan of mice.
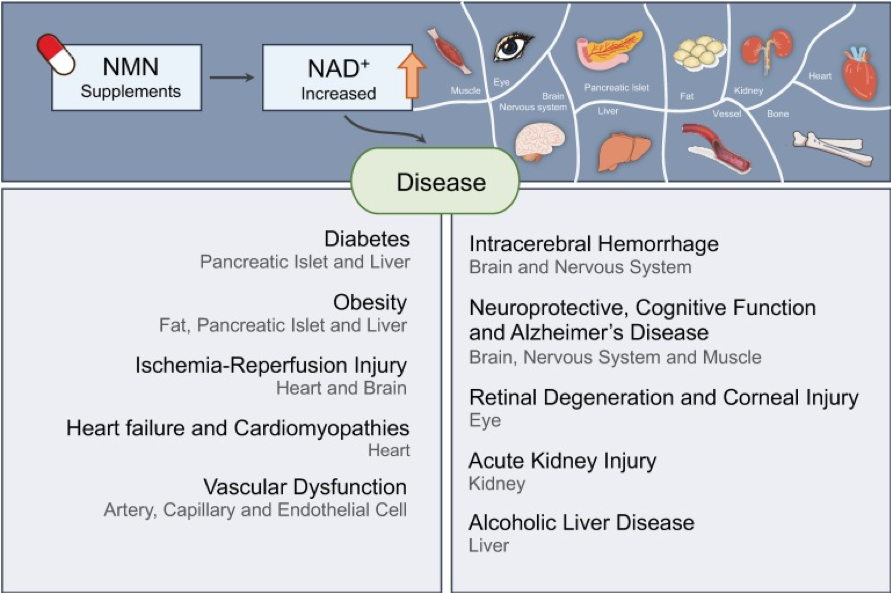
Recommended Dose for Human Consumption
Research in animal studies has shown that increasing NAD+ levels can reverse various age-related illnesses such as heart diseases, diabetes, and neurodegeneration. Boosting the molecule even extended the lifespans of yeast, worms, and mice. NMN’s NAD+-boosting ability in animals and its healthspan-promoting properties led scientists to believe in the molecule’s therapeutic potentials. Now, scientists are starting clinical trials to understand whether NMN is safe, how much we should take, and what it does to our body.
Clinical Trials on Safety of NMN
An international team of researchers ran the first human clinical study for NMN in Japan to investigate the safety of the molecule. Although the size of the Phase 1 clinical trial was small, the study showed that dosages up to 500 mg of orally administered NMN are safe in humans, implicating a potential therapeutic strategy. The results appeared in the journal Endocrine, November 2019.
NMN’s safety as a dietary supplement has been proven in a number of FDA-approved clinical trials.
Other clinical trials registered with the World Health Organization (WHO) are also examining the safety and efficacy of NMN. In the US, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine are running a clinical trial to test NMN’s effect on cardiovascular and metabolic health with a daily dosage of 250 mg. Another clinical study at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston is also testing the supplement’s effects on the body and if there are any side effects.
Although researchers still need to conduct more studies to determine the efficient dosage for humans, clinical trials of other NAD boosters have shown that 1 gram of oral supplement every day can stimulate NAD+ metabolism in healthy middle-aged and older adults.
Do Scientists Use NMN?
With clinical studies still underway, some scientists are confident enough in NAD+’s benefits for aging and are already taking supplements themselves.
David Sinclair, a Harvard professor who studies aging, talked about taking NMN to remain healthy and prevent aging on The Joe Rogan Experience podcast. Sinclair takes 1 gram of NMN every day, along with other supplements including resveratrol, metformin, and aspirin. When asked if there are any downsides of the supplements, Sinclair said he hasn’t experienced anything other than stomach upset so far, and to him, “anything’s better than what’s coming” — aging.
Side Effects of NMN Supplementation
Currently, no side effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide have been documented in humans. Researchers have conducted the majority of studies on NMN in rodents, which revealed positive effects on metabolism, brain function, liver, skin, muscle, bone structure, heart health, reproduction, immunity, and lifespan. Long-term mice study also showed no toxicity, serious side effects, or increased mortality rate throughout the 12 month intervention period.
A single study of NMN in humans reveals no safety concerns following single oral doses of 100, 250, and 500 mg of NMN. Five hours following the single oral administration of NMN, scientists found no changes in heart rate, blood pressure, blood oxygen levels, or body temperature. Laboratory analyses of blood did not show significant changes, except with levels of four molecules in the blood, which fell within normal ranges. This study also measured sleep quality and found no differences before and after the NMN consumption.
Scientists need to conduct further studies of NMN administration in humans to determine whether side effects come from consuming it. Scientists could look at doses higher than 500 mg to find whether they induce side effects. Research could also look at whether long-term consumption of NMN causes side effects.
Active NMN Clinical Trials
Since NMN has benefits in various mouse models of human disease, several clinical trials of NMN have been conducted to investigate its clinical applicability
Future NMN Research
Recounted by various nations around the world for thousands of years, emperors and kings alike searched every corner they could reach for the Fountain of Youth. The tale remains a mystery to this day, but instead of explorers, scientists are on the quest.
Studies in animals showed NMN’s promising properties in NAD+-boosting and anti-aging. Now, researchers are moving forward with clinical trials to investigate the safety and efficacy of the molecule in humans. With the research efforts that are pouring into the field of anti-aging by institutions and private entities, researchers will start getting answers soon. To scientists, the ultimate goal is to develop treatments that slow, stop or even reverse aging — for people to live a long and healthy life.
Taking NMN may provide a promising means to combat age-related diseases and ailments. Below is a summary of major studies elucidating the potential benefits of NMN.
| Research Category | Summary / Conclusion | Mouse / Rat | Human | Pig |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone Repair | ||||
| Cancer |
| |||
| Cardiovascular |
| |||
| DNA Repair |
| |||
| Eye Protection | ||||
| Immunity |
| |||
| Longevity |
| |||
| Metabolism |
| |||
| Neurological |
| |||
| Reproduction | ||||
| Skin and Muscle | ||||
| Organ Health |
| |||
| Mechanism |
|
Reference Links
- Alessia Grozio, Kathryn F. Mills, Jun Yoshino, Santina Bruzzone, Giovanna Sociali, Kyohei Tokizane, Hanyue Cecilia Lei, Richard Cunningham, Yo Sasaki, Marie E. Migaud, Shin-ichiro Imai. Slc12a8 is a nicotinamide mononucleotide transporter. Nat Metab, 2019; DOI: 10.1038/s42255-018-0009-4.
- Huang RX, Tao J. Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates glucocorticoid-induced osteogenic inhibition by regulating the SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(1):145-154. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11116
- Lv H, Lv G, Chen C, Zong Q, Jiang G, Ye D, Cui X, He Y, Xiang W, Han Q, Tang L, Yang W, Wang H. NAD+ Metabolism Maintains Inducible PD-L1 Expression to Drive Tumor Immune Evasion. Cell Metab. 2020 Nov 9. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.021
- Martin AS, Abraham DM, Hershberger KA, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide requires SIRT3 to improve cardiac function and bioenergetics in a Friedreich’s ataxia cardiomyopathy model. JCI Insight. 2017;2(14):e93885. Published 2017 Jul 20. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.93885
- Hisayuki Amano, Arindam Chaudhury, Cristian Rodriguez-Aguayo, Lan Lu, Viktor Akhanov, Andre Catic, Yury V. Popov, Eric Verdin, Hannah Johnson, Fabio Stossi, David A. Sinclair, Eiko Nakamaru-Ogiso, Gabriel Lopez-Berestein, Jeffrey T. Chang, Joel R. Neilson, Alan Meeker, Milton Finegold, Joseph A. Baur, Ergun Sahin. Telomere dysfunction induces sirtuin repression that drives telomere-dependent disease. Cell Metab, 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.03.001.
- Chen X, Amorim JA, Moustafa GA, Lee JJ, Yu Z, Ishihara K, Iesato Y, Barbisan P, Ueta T, Togka KA, Lu L, Sinclair DA, Vavvas DG. Neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of action of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) in a photoreceptor degenerative model of retinal detachment. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 29;12. doi: 10.18632/aging.202453. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33373320.
- Omran HM, Almaliki MS. Influence of NAD+ as an ageing-related immunomodulator on COVID 19 infection: A hypothesis. J Infect Public Health. 2020 Sep;13(9):1196-1201. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.004. Epub 2020 Jun 7. PMID: 32534944; PMCID: PMC7275989.
- Yoshida M, Satoh A, Lin JB, et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Contained eNAMPT Delays Aging and Extends Lifespan in Mice. Cell Metab. 2019;30(2):329-342.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.05.015
- Yoshino M, Yoshino J, Kayser BD, Patti G, Franczyk MP, Mills KF, Sindelar M, Pietka T, Patterson BW, Imai SI, Klein S. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science. 2021 Apr 22:eabe9985. doi: 10.1126/science.abe9985. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33888596.
- Sanli Xing, Yiran Hu, Xujiao Huang, Dingzhu Shen, Chuan Chen. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase related signalling pathway in early Alzheimer’s disease mouse models.Shanghai Geriatric Institute of Chinese Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200031, P.R. China (2019) doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10782
- Xie X, Yu C, Zhou J, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates the depression-like behaviors and is associated with attenuating the disruption of mitochondrial bioenergetics in depressed mice. J Affect Disord. 2020;263:166-174. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.147
- Liang Shu, Xiaolei Shen, Yaxue Zhao, Xinwei He, Jiawen Yin, Jingjing Su, Qiang Li, Jianren Liu. Mechanisms of transformation of nicotinamide mononucleotides to cerebral infarction hemorrhage based on MCAO model. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2020; DOI: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.023.
- Yang L, Lin X, Tang H, Fan Y, Zeng S, Jia L, Li Y, Shi Y, He S, Wang H, Hu Z, Gong X, Liang X, Yang Y, Liu X. Mitochondrial DNA mutation exacerbates female reproductive aging via impairment of the NADH/NAD+ redox. Aging Cell. 2020 Sep;19(9):e13206. doi: 10.1111/acel.13206.
- Assiri MA, Ali HR, Marentette JO, Yun Y, Liu J, Hirschey MD, Saba LM, Harris PS, and Fritz KS. Investigating RNA expression profiles altered by nicotinamide mononucleotide therapy in a chronic model of alcoholic liver disease. Hum Genomics, 2019; DOI: 10.1186/s40246-019-0251-1.
- Jia Y, Kang X, Tan L, Ren Y, Qu L, Tang J, Liu G, Wang S, Xiong Z and Yang L (2021) Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Attenuates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis After AKI by Suppressing Tubular DNA Damage and Senescence. Front. Physiol. 12:649547. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.649547
- Zong Z, Liu J, Wang N, Yang C, Wang Q, Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu X, Deng H. Nicotinamide mononucleotide inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation to prevent liver fibrosis via promoting PGE2 degradation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020 Nov 19:S0891-5849(20)31626-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.11.014. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33220424.
- Meng YF, Pu Q, Dai SY, Ma Q, Li X, Zhu W. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Hyperosmolarity-Induced IL-17a Secretion and Macrophage Activation in Corneal Epithelial Cells/Macrophage Co-Culture System. J Inflamm Res. 2021 Feb 22;14:479-493. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S292764. PMID: 33658825; PMCID: PMC7917392.
- Li J, Bonkowski MS, Moniot S, et al. A conserved NAD+ binding pocket that regulates protein-protein interactions during aging. Science. 2017;355(6331):1312-1317. doi:10.1126/science.aad8242
- Miao Y, Li X, Shi X, Gao Q, Chen J, Wang R, Fan Y, Xiong B. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Restores the Meiotic Competency of Porcine Oocytes Exposed to Ethylene Glycol Butyl Ether. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Feb 2;9:628580. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.628580.
- Mills et al., 2016, Cell Metabolism 24, 795–806, December 13, 2016 ª 2016 Elsevier Inc. DOI: doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.013
- Gomes AP, Price NL, Ling AJ, et al. Declining NAD(+) induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging. Cell. 2013;155(7):1624-1638. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.037
- Yamamoto T, Byun J, Zhai P, Ikeda Y, Oka S, et al. (2014) Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, an Intermediate of NAD+ Synthesis, Protects the Heart from Ischemia and Reperfusion. PLoS ONE 9(6): e98972. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098972
- de Picciotto NE, Gano LB, Johnson LC, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation reverses vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress with aging in mice. Aging Cell. 2016;15(3):522-530. doi:10.1111/acel.12461
- Keisuke Okabe, Keisuke Yaku, Kazuyuki Tobe, Takashi Nakagawa. Implications of altered NAD metabolism in metabolic disorders. J Biomed Sci, 2019; DOI: 10.1186/s12929-019-0527-8.
- Uddin GM, Youngson NA, Sinclair DA, Morris MJ. Head to Head Comparison of Short-Term Treatment with the NAD(+) Precursor Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) and 6 Weeks of Exercise in Obese Female Mice. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:258. Published 2016 Aug 19. doi:10.3389/fphar.2016.00258
- Uchida R, Saito Y, Nogami K, et al. Epigenetic silencing of Lgr5 induces senescence of intestinal epithelial organoids during the process of aging [published correction appears in NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2019 Mar 7;5:5]. NPJ Aging Mech Dis. 2018;5:1. Published 2018 Dec 1. doi: 10.1038/s41514-018-0031-5
- Li Y, Ma X, Li J, et al. Corneal denervation causes epithelial apoptosis through inhibiting NAD. biosynthesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:3538–3546. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.19-26909
- Yoo KH, Tang JJ, Rashid MA, Cho CH, Corujo-Ramirez A, Choi J, Bae MG, Brogren D, Hawse JR, Hou X, Weroha SJ, Oliveros A, Kirkeby LA, Baur JA, Jang MH. Nicotinamide mononucleotide prevents cisplatin-induced cognitive impairments. Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 26:canres.3290.2020. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3290.
- Forte M, Bianchi F, Cotugno M, Marchitti S, De Falco E, Raffa S, Stanzione R, Di Nonno F, Chimenti I, Palmerio S, Pagano F, Petrozza V, Micaloni A, Madonna M, Relucenti M, Torrisi MR, Frati G, Volpe M, Rubattu S, Sciarretta S. Pharmacological restoration of autophagy reduces hypertension-related stroke occurrence. Autophagy. 2020 Aug;16(8):1468-1481. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1687215. Epub 2019 Nov 12. PMID: 31679456; PMCID: PMC7469607.
- Li B, Shi Y, Liu M, Wu F, Hu X, Yu F, Wang C, Ye L. Attenuates of NAD+ impair BMSC osteogenesis and fracture repair through OXPHOS. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Feb 22;13(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02748-9. PMID: 35193674; PMCID: PMC8864833.
- Hu M, Xing L, Zhang L, Liu F, Wang S, Xie Y, Wang J, Jiang H, Guo J, Li X, Wang J, Sui L, Li C, Liu D, Liu Z. NAP1L2 drives mesenchymal stem cell senescence and suppresses osteogenic differentiation. Aging Cell. 2022 Jan 15:e13551. doi: 10.1111/acel.13551. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35032339.
- Song J, Li J, Yang F, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide promotes osteogenesis and reduces adipogenesis by regulating mesenchymal stromal cells via the SIRT1 pathway in aged bone marrow. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):336. Published 2019 Apr 18. doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1569-2
- Yoo KH, Tang JJ, Rashid MA, Cho CH, Corujo-Ramirez A, Choi J, Bae MG, Brogren D, Hawse JR, Hou X, Weroha SJ, Oliveros A, Kirkeby LA, Baur JA, Jang MH. Nicotinamide mononucleotide prevents cisplatin-induced cognitive impairments. Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 26:canres.3290.2020. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-3290.
- Zhen Yu, Shuai Tong, Can Zhang et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide enhances the efficacy and persistence of CD19 CAR-T cells via NAD + –Sirt1 axis, 19 April 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1483519/v1]
- Khosroshahi AJ, Mokhtari B, Badalzadeh R. Combination of nicotinamide mononucleotide and troxerutin induces full protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating mitochondrial biogenesis and inflammatory response. Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul 17. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07390-5. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35842854.
- Gan L, Liu D, Liu J, Chen E, Chen C, Liu L, Hu H, Guan X, Ma W, Zhang Y, He Y, Liu B, Tang S, Jiang W, Xue J, Xin H. CD38 deficiency alleviates Ang II-induced vascular remodeling by inhibiting small extracellular vesicle-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell senescence in mice. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jun 11;6(1):223. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00625-0. PMID: 34112762.
- Sun L, Zhang W. Preconditioning of mesenchymal stem cells with ghrelin exerts superior cardioprotection in aged heart through boosting mitochondrial function and autophagy flux. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 May 2;903:174142. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174142.
- Whitson JA, Bitto A, Zhang H, Sweetwyne MT, Coig R, Bhayana S, Shankland EG, Wang L, Bammler TK, Mills KF, Imai SI, Conley KE, Marcinek DJ, Rabinovitch PS. SS-31 and NMN: Two paths to improve metabolism and function in aged hearts. Aging Cell. 2020 Aug 11:e13213. doi: 10.1111/acel.13213. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 32779818.
- Hosseini L, Vafaee MS, Badalzadeh R. Melatonin and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Attenuate Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Modulation of Mitochondrial Function and Hemodynamic Parameters in Aged Rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2020 May;25(3):240-250. doi: 10.1177/1074248419882002.
- Zhang R, Shen Y, Zhou L, et al. Short-term administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide preserves cardiac mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017;112:64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.09.001
- Sasaki, L., Hamada, Y., Yarimizu, D. et al. Intracrine activity involving NAD-dependent circadian steroidogenic activity governs age-associated meibomian gland dysfunction. Nat Aging 2, 105–114 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s43587-021-00167-8
- Guo X, Tan S, Wang T, Sun R, Li S, Tian P, Li M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Yan Y, Dong Z, Yan L, Yue X, Wu Z, Li C, Yamagata K, Gao L, Ma C, Li T, Liang X. NAD+ salvage governs mitochondrial metabolism, invigorating natural killer cell antitumor immunity. Hepatology. 2022 Jul 11. doi: 10.1002/hep.32658. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35815363.
- Nomiyama T, Setoyama D, Yasukawa T, Kang D. Mitochondria Metabolomics Reveals a Role of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Metabolism in Mitochondrial DNA Replication. J Biochem. 2021 Dec 4:mvab136. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvab136. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34865026.
- Hunt NJ, Lockwood GP, Kang SWS, Westwood LJ, Limantoro C, Chrzanowski W, McCourt PAG, Kuncic Z, Le Couteur DG, Cogger VC. Quantum Dot Nanomedicine Formulations Dramatically Improve Pharmacological Properties and Alter Uptake Pathways of Metformin and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Aging Mice. ACS Nano. 2021 Feb 24. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09278. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33626869.
- Uddin GM, Youngson NA, Chowdhury SS, Hagan C, Sinclair DA, Morris MJ. Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) Reduces Metabolic Impairment in Male Mouse Offspring from Obese Mothers. Cells. 2020 Mar 25;9(4):791. doi: 10.3390/cells9040791.
- Kim HW, Ryoo GH, Jang HY, Rah SY, Lee DH, Kim DK, Bae EJ, Park BH. NAD+-boosting molecules suppress mast cell degranulation and anaphylactic responses in mice. Theranostics. 2022 Apr 11;12(7):3316-3328. doi: 10.7150/thno.69684. PMID: 35547746; PMCID: PMC9065190.
- Liu J, Zong Z, Zhang W, Chen Y, Wang X, Shen J, Yang C, Liu X, Deng H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Oxidative Stress via Decreasing COX-2 Expression in Macrophages. Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Jul 6;8:702107. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.702107. PMID: 34295923; PMCID: PMC8290259.
- Niu KM, Bao T, Gao L, Ru M, Li Y, Jiang L, Ye C, Wang S, Wu X. The Impacts of Short-Term NMN Supplementation on Serum Metabolism, Fecal Microbiota, and Telomere Length in Pre-Aging Phase. Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 29;8:756243. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.756243. PMID: 34912838; PMCID: PMC8667784.
- Xiaonan Wang, Wuejun Hu, Yang Yang, Toshihiro Takata, Takashi Sakurai. Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against ß-amyloid oligomer-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal death. Brain Res, 2016; DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.060.
- Chandrasekaran K, Najimi N, Sagi AR, Yarlagadda S, Salimian M, Arvas MI, Hedayat AF, Kevas Y, Kadakia A, Russell JW. NAD+ Precursors Repair Mitochondrial Function in Diabetes and Prevent Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 28;23(9):4887. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094887. PMID: 35563288; PMCID: PMC9102948.
- Stefano Tarantini, Marta Noa Valcarcel-Ares, Peter Toth, Andriy Yabluchanskiy, Zsuzsanna Tucsek, Tamas Kiss, Peter Hertelendy, Michael Kinter, Praveen Ballabh, Zoltan Sule, Eszter Farkas, Joseph A. Baur, David A. Sinclair, Anna Csistzar, Zoltan Ungvari. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function inn aged mice. Redox Biol, 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192.
- Tamas Kiss, Priya Balasubramanian, Marta Noa Valcarcel-Ares, Stefano Tarantini, Andriy Yabluchanskiy, Tamas Csipo, Agnes Lipecz, Dora Reglodi, Xin A. Zhang, Ferenc Bari, Eszter Farkas, Anna Csiszar, Zoltan Ungvari. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) treatment attenuates oxidative stress and rescues angiogenic capacity in aged cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells: a potential mechanism for the prevention of vascular cognitive impairment. Geroscience, 2019; DOI: 10.1007/s11357-019-00074-2.
- Leila Hosseini, Fatemeh Farokhi-Sisakht, Reza Badalzadeh, Aytak Khabbaz, Javad Mahmoudi, Saeed Sadigh-Eteghad. Nicotinamide mononucleotide and melatonin alleviate aging-induced cognitive impairment via modulation of mitochondrial function and apoptosis in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience, 2019; DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.09.037.
- Klimova N, Fearnow A, Long A, Kristian T. NAD+ precursor modulates post-ischemic mitochondrial fragmentation and reactive oxygen species generation via SIRT3 dependent mechanisms. Exp Neurol. 2020;325:113144. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113144
- Kiss T, Nyúl-Tóth Á, Balasubramanian P, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. Geroscience. 2020;42(2):527-546. doi:10.1007/s11357-020-00165-5
- Chandrasekaran K, Choi J, Arvas MI, Salimian M, Singh S, Xu S, Gullapalli RP, Kristian T, Russell JW. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Administration Prevents Experimental Diabetes-Induced Cognitive Impairment and Loss of Hippocampal Neurons. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 26;21(11):3756. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113756. PMID: 32466541; PMCID: PMC7313029.
- Deng, X., Liang, X., Yang, H., Huang, Z., Huang, X., Liang, C., Kuang, Y., Qin, Y., Lin, F. and Luo, Z. (2020), Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) protects bEnd.3 cells against H2O2‐induced damage via NAMPT and the NF‐κB p65 signalling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. Accepted Author Manuscript. DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13067
- Chandrasekaran K, Najimi N, Sagi AR, Yarlagadda S, Salimian M, Arvas MI, Hedayat AF, Kevas Y, Kadakia A, Russell JW. NAD+ Precursors Repair Mitochondrial Function in Diabetes and Prevent Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 28;23(9):4887. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094887. PMID: 35563288; PMCID: PMC9102948.
- Yu M, Zheng X, Cheng F, Shao B, Zhuge Q, Jin K. Metformin, Rapamycin, or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Pretreatment Attenuate Cognitive Impairment After Cerebral Hypoperfusion by Inhibiting Microglial Phagocytosis. Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 13;13:903565. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.903565. PMID: 35769369; PMCID: PMC9234123.
- Hu Y, Huang Y, Xing S, Chen C, Shen D, Chen J. Aβ promotes CD38 expression in senescent microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Res. 2022 Mar 3;55(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00379-1. PMID: 35241173; PMCID: PMC8892694.
- Liu X, Dilxat T, Shi Q, Qiu T, Lin J. The combination of nicotinamide mononucleotide and lycopene prevents cognitive impairment and attenuates oxidative damage in D-galactose induced aging models via Keap1-Nrf2 signaling. Gene. 2022 May 15;822:146348. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2022.146348. Epub 2022 Feb 17. PMID: 35183682.Mode
- Miao Y, Cui Z, Gao Q, Rui R, Xiong B. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Reverses the Declining Quality of Maternally Aged Oocytes. Cell Rep. 2020 Aug 4;32(5):107987. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107987. PMID: 32755581.
- Wang L, Chen Y, Wei J, Guo F, Li L, Han Z, Wang Z, Zhu H, Zhang X, Li Z, Dai X. Administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide improves oocyte quality of obese mice. Cell Prolif. 2022 Jul 10:e13303. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13303. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35811338.
- Yoshino M, Yoshino J, Kayser BD, Patti G, Franczyk MP, Mills KF, Sindelar M, Pietka T, Patterson BW, Imai SI, Klein S. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science. 2021 Apr 22:eabe9985. doi: 10.1126/science.abe9985. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33888596.
- Masaki Igarashi, Masaomi Miura, Yoshiko Nakagawa-Nagahama et al. Chronic nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation elevates blood nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide levels and alters muscle motility in healthy old men, 09 June 2021. DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-455083/v1
- Katayoshi T, Nakajo T, Tsuji-Naito K. Restoring NAD+ by NAMPT is essential for the SIRT1/p53-mediated survival of UVA- and UVB-irradiated epidermal keratinocytes. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2021 Jun 12;221:112238. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112238. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34130091.
- Liao B, Zhao Y, Wang D, Zhang X, Hao X, Hu M. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021 Jul 8;18(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00442-4. PMID: 34238308; PMCID: PMC8265078.
- Ito N, Takatsu A, Ito H, Koike Y, Yoshioka K, Kamei Y, Imai SI. Slc12a8 in the lateral hypothalamus maintains energy metabolism and skeletal muscle functions during aging. Cell Rep. 2022 Jul 26;40(4):111131. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111131. PMID: 35905718.
- Gao JF, Tang L, Luo F, Zhang YY, Chen L, Ding H, Meng ZD. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice by blocking activation of ROS-mediated JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108812. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108812. Epub 2022 May 6. PMID: 35533554.
- Yasuda I, Hasegawa K, Sakamaki Y, Muraoka H, Kawaguchi T, Kusahana E, Ono T, Kanda T, Tokuyama H, Wakino S, Itoh H. Pre-emptive Short-term Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Treatment in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jun 1;32(6):1355-1370. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020081188.
- Ru M, Wang W, Zhai Z, Wang R, Li Y, Liang J, Kothari D, Niu K, Wu X. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation protects the intestinal function in aging mice and D-galactose induced senescent cells. Food Funct. 2022 Jul 18;13(14):7507-7519. doi: 10.1039/d2fo00525e. PMID: 35678708.
- Yi M, Ma Y, Zhu S, Luo C, Chen Y, Wang Q, Deng H. Comparative proteomic analysis identifies biomarkers for renal aging. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 6;12(21):21890-21903. doi: 10.18632/aging.104007. Epub 2020 Nov 6. PMID: 33159023; PMCID: PMC7695359.
- Murata MM, Kong X, Moncada E, Chen Y, Imamura H, Wang P, Berns MW, Yokomori K, Digman MA. NAD+ consumption by PARP1 in response to DNA damage triggers metabolic shift critical for damaged cell survival. Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Sep 15;30(20):2584-2597. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-10-0650. Epub 2019 Aug 7. PMID: 31390283; PMCID: PMC6740200.
- Mateuszuk Ł, Campagna R, Kutryb-Zając B, Kuś K, Słominska EM, Smolenski RT, Chlopicki S. Reversal of endothelial dysfunction by nicotinamide mononucleotide via extracellular conversion to nicotinamide riboside. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Aug;178:114019. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114019.
- Gao JF, Tang L, Luo F, Zhang YY, Chen L, Ding H, Meng ZD. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates DNFB-induced atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice by blocking activation of ROS-mediated JAK2/STAT5 signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108812. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108812. Epub 2022 May 6. PMID: 35533554.
- Ren C, Hu C, Wu Y, Li T, Zou A, Yu D, Shen T, Cai W, Yu J. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Cellular Senescence and Inflammation Caused by Sodium Iodate in RPE. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 18;2022:5961123. doi: 10.1155/2022/5961123. PMID: 35898618; PMCID: PMC9313989.
- Hasegawa K, Sakamaki Y, Tamaki M, Wakino S. Nicotinamide mononucleotide ameliorates adriamycin-induced renal damage by epigenetically suppressing the NMN/NAD consumers mediated by Twist2. Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18147-2. PMID: 35962139; PMCID: PMC9374671.
- Chang TM, Yang TY, Huang HC. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide and Coenzyme Q10 Protects Fibroblast Senescence Induced by Particulate Matter Preconditioned Mast Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 7;23(14):7539. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147539. PMID: 35886889; PMCID: PMC9319393.
- Ma D, Hu L, Wang J, Luo M, Liang A, Lei X, Liao B, Li M, Xie M, Li H, Gong Y, Zi D, Li X, Chen X, Liao X. Nicotinamide mononucleotide improves spermatogenic function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice via modulating the glycolysis pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Jul 25. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022099. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35929593.
- Takeshi Katayoshi, Sachi Uehata, Noe Nakashima et al. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism and arterial stiffness after long-term nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 29 July 2022, PREPRINT (Version 1) available at Research Square [https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1802944/v1]
- Kimura S, Ichikawa M, Sugawara S, et al. (September 05, 2022) Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Is Safely Metabolized and Significantly Reduces Blood Triglyceride Levels in Healthy Individuals. Cureus 14(9): e28812. doi:10.7759/cureus.28812
- Pan Huang, Xuxin Wang, Siyu Wang, Zhipeng Wu, Zhengrong Zhou, Genbao Shao, Caifang Ren, Meiqian Kuang, Yan Zhou, Anqi Jiang, Weihong Tang, Jianye Miao, Xin Qian, Aihua Gong, Min Xu. Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: Potential effect of NMN on intestinal barrier and gut microbiota. Current Research in Food Science, Volume 5, 2022, Pages 1403 1411. ISSN 2665-9271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crfs.2022.08.011.
- Aflatounian A, Paris VR, Richani D, Edwards MC, Cochran BJ, Ledger WL, Gilchrist RB, Bertoldo MJ, Wu LE, Walters KA. Declining muscle NAD+ in a hyperandrogenism PCOS mouse model: Possible role in metabolic dysregulation. Mol Metab. 2022 Sep 9;65:101583. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101583. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36096453; PMCID: PMC9490589.
- Setoyama, Daiki and Nomiyama, Tomoko and Yamamoto, Masamichi and Kang, Dongchon, β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Increases the Nucleotide Pool Through Multiple Pathways, Improving Mitochondrial DNA Metabolism. Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4227260 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4227260
- Lee D, Tomita Y, Miwa Y, Shinojima A, Ban N, Yamaguchi S, Nishioka K, Negishi K, Yoshino J, Kurihara T. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Prevents Retinal Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Retinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(19):11228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911228
- Luo C, Ding W, Yang C, Zhang W, Liu X, Deng H. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Administration Restores Redox Homeostasis via the Sirt3-Nrf2 Axis and Protects Aged Mice from Oxidative Stress-Induced Liver Injury. J Proteome Res. 2022 Jul 1;21(7):1759-1770. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00167. Epub 2022 Jun 14. PMID: 35699728.
- Jin R, Niu C, Wu F, Zhou S, Han T, Zhang Z, Li E, Zhang X, Xu S, Wang J, Tian S, Chen W, Ye Q, Cao C, Cheng L. DNA damage contributes to age-associated differences in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Aging Cell. 2022 Oct 18:e13729. doi: 10.1111/acel.13729. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36254583.
- Zhao X, Zhang M, Wang J, Ji K, Wang Y, Sun X, Xu C, Wang Q, He N, Song H, Du L, Wang F, Huang H, Liu Y, Liu Q. NMN ameliorated radiation induced damage in NRF2-deficient cell and mice via regulating SIRT6 and SIRT7. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Oct 14:S0891-5849(22)00897-8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.10.267. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36252808.
- Shen X, Wu B, Jiang W, Li Y, Zhang Y, Zhao K, Nie N, Gong L, Liu Y, Zou X, Liu J, Jin J, Ouyang H. Scale bar of aging trajectories for screening personal rejuvenation treatments. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 21;20:5750-5760. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.021. PMID: 36382193; PMCID: PMC9619353.
- Wong W, Crane ED, Zhang H, Li J, Day TA, Green AE, Menzies KJ, Crane JD. Pgc-1α controls epidermal stem cell fate and skin repair by sustaining NAD+ homeostasis during aging. Mol Metab. 2022 Nov;65:101575. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101575. Epub 2022 Aug 17. PMID: 35987498; PMCID: PMC9463389.
- Yi L, Maier AB, Tao R, Lin Z, Vaidya A, Pendse S, Thasma S, Andhalkar N, Avhad G, Kumbhar V. The efficacy and safety of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial. Geroscience. 2022 Dec 8. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00705-1. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36482258.
- Lee, D.; Tomita, Y.; Miwa, Y.; Jeong, H.; Shinojima, A.; Ban, N.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nishioka, K.; Negishi, K.; Yoshino, J.; Kurihara, T. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Protects against Retinal Dysfunction in a Murine Model of Carotid Artery Occlusion.Int. J. Mol. Sci.2022,23, 14711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314711
- Tian Y, Zhu CL, Li P, Li HR, Liu Q, Deng XM, Wang JF. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Attenuates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury With Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Apoptotic Effects. J Surg Res. 2022 Nov 5;283:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2022.09.030. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36347171.
- ZHAO, B., Liu, C., Qiang, L., Liu, J., Qiu, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Li, Y., & Zhang, M. (2022). Clinical observation of the effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on the improvement of insomnia in middle-aged and old adults. American Journal of Translational Medicine, 6(4), 167–176.
- Wang H, Sun Y, Pi C, Yu X, Gao X, Zhang C, Sun H, Zhang H, Shi Y, He X. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Improves Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Rescues Cellular Senescence by NAD+/Sirt3 Pathway in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(23):14739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314739
- Margier M, Kuehnemann C, Hulo N, Morales J, Ashok Kumaar PV, Cros C, Cannelle H, Charmetant J, Verdin E, Canault M, Grozio A. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Administration Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity and Loss in Physical Activity in Mice. Cells. 2022 Dec 27;12(1):108. doi: 10.3390/cells12010108. PMID: 36611902; PMCID: PMC9818647.
- Wang L, Zhao M, Qian R, Wang M, Bao Q, Chen X, Du W, Zhang L, Ye T, Xie Y, Zhang B, Peng L, Yao Y. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010143
- Jiang Y, Luo Z, Gong Y, Fu Y, Luo Y. NAD+ supplementation limits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis via SIRT1-P66Shc signaling. Oncogene. 2023 Jan 23. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02592-y. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36690678.
- Fang D, Xu T, Sun J, Shi J, Li F, Yin Y, Wang Z, Liu Y. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Sleep Deprivation-Induced Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis and Restores Colonization Resistance against Intestinal Infections. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Jan 25:e2207170. doi: 10.1002/advs.202207170. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36698264.
- Zhu X, Cheng J, Yu J, Liu R, Ma H, Zhao Y. Nicotinamide mononucleotides alleviated neurological impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury. Int J Med Sci 2023; 20(3):307-317. doi:10.7150/ijms.80942. https://www.medsci.org/v20p0307.htm
- Rashid MA, Oliveros A, Kim YS, Jang MH. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Mitochondrial Defects in Cortical Neurons Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Brain Plast. 2022 Dec 20;8(2):143-152. doi: 10.3233/BPL-220143. PMID: 36721392; PMCID: PMC9837732.
- Wu K, Li B, Ma Y, Tu T, Lin Q, Zhu J, Zhou Y, Liu N, Liu Q. Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates HIF-1α activation and fibrosis in hypoxic adipose tissue via NAD+/SIRT1 axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 26;14:1099134. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1099134. PMID: 36777361; PMCID: PMC9909340.
- Jiang Y, Wang D, Zhang C, Jiao Y, Pu Y, Cheng R, Li C, Chen Y. Nicotinamide mononucleotide restores oxidative stress-related apoptosis of oocyte exposed to benzyl butyl phthalate in mice. Cell Prolif. 2023 Feb 9:e13419. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13419. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36756972.
- Montali I, Berti CC, Morselli M, Acerbi G, Barili V, Pedrazzi G, Montanini B, Boni C, Alfieri A, Pesci M, Loglio A, Degasperi E, Borghi M, Perbellini R, Penna A, Laccabue D, Rossi M, Vecchi A, Tiezzi C, Reverberi V, Boarini C, Abbati G, Massari M, Lampertico P, Missale G, Ferrari C, Fisicaro P. Deregulated intracellular pathways define novel molecular targets for HBV-specific CD8 T cell reconstitution in chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 2023 Mar 7:S0168-8278(23)00167-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2023.02.035. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36893853.
- Huang Y, Dou Y, Yang B, He B, Zhang X, Zhang K, Yang X. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation mitigates osteopenia induced by modeled microgravity in rats. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 May 17. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01356-7. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37195399.
- Huang H, Shi J, Li Z, Rang Y, Li W, Xiao X, Chen C, Liu C. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) ameliorated Nonylphenol-induced learning and memory impairment in rats via the central 5-HT system and the NAD+/SIRT1/MAO-A pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2023 Jun 7:113878. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2023.113878. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37295765.
- Yamane T, Imai M, Bamba T, Uchiyama S. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) intake increases plasma NMN and insulin levels in healthy subjects. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2023 Aug;56:83-86. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.04.031. Epub 2023 May 5. PMID: 37344088.
- Li, H., Liu, Q., Zhu, C., Sun, X., Sun, C., Yu, C., Li, P., Deng, X., & Wang, J. (2023). β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide activates NAD+/SIRT1 pathway and attenuates inflammatory and oxidative responses in the hippocampus regions of septic mice. Redox Biology, 63, 102745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2023.102745
- Pencina KM, Valderrabano R, Wipper B, Orkaby AR, Reid KF, Storer T, Lin AP, Merugumala S, Wilson L, Latham N, Ghattas-Puylara C, Ozimek NE, Cheng M, Bhargava A, Memish-Beleva Y, Lawney B, Lavu S, Swain PM, Apte RS, Sinclair DA, Livingston D, Bhasin S. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Augmentation in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Physiologic Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Feb 6:dgad027. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad027. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36740954.
- Zhang R, Chen S, Wang Z, Ye L, Jiang Y, Li M, Jiang X, Peng H, Guo Z, Chen L, Zhang R, Niu Y, Aschner M, Li D, Chen W. Assessing the Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation on Pulmonary Inflammation in Male Mice Subchronically Exposed to Ambient Particulate Matter. Environ Health Perspect. 2023 Jul;131(7):77006. doi: 10.1289/EHP12259. Epub 2023 Jul 17. PMID: 37458712; PMCID: PMC10351503.
- Sano, H., Kratz, A., Nishino, T., Imamura, H., Yoshida, Y., Shimizu, N., Kitano, H., & Yachie, A. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) alleviates the poly(I:C)-induced inflammatory response in human primary cell cultures. Scientific Reports, 13(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38762-x
- Ur Rahman S, Qadeer A, Wu Z. Role and Potential Mechanisms of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Aging. Aging Dis. 2023 Jul 27. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0519-1. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37548938.
- Freeberg, K. A., Ludwig, K. R., Chonchol, M., Seals, D. R., & Rossman, M. J. (2023). NAD+-boosting compounds enhance nitric oxide production and prevent oxidative stress in endothelial cells exposed to plasma from patients with COVID-19. Nitric Oxide. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2023.08.003
- Zhan R, Meng X, Tian D, Xu J, Cui H, Yang J, Xu Y, Shi M, Xue J, Yu W, Hu G, Li K, Ge X, Zhang Q, Zhao M, Du J, Guo X, Xu W, Gao Y, Yao C, Chen F, Chen Y, Shan W, Zhu Y, Ji L, Pan B, Yu Y, Li W, Zhao X, He Q, Liu X, Huang Y, Liao S, Zhou B, Chui D, Chen YE, Sun Z, Dong E, Wang Y, Zheng L. NAD+ rescues aging-induced blood-brain barrier damage via the CX43-PARP1 axis. Neuron. 2023 Aug 29:S0896-6273(23)00622-0. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.010. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37683629.
- Liang Y, Li M, Tang Y, Yang J, Wang J, Zhu Y, Liang H, Lin Q, Cheng Y, Yang X, Zhu H. Temperature-sensitive hydrogel dressing loaded with nicotinamide mononucleotide accelerating wound healing in diabetic mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep 7;167:115431. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115431. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37688988.
- Qiu, Y., Xu, S., Chen, X. et al. NAD+ exhaustion by CD38 upregulation contributes to blood pressure elevation and vascular damage in hypertension. Sig Transduct Target Ther 8, 353 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01577-3
- Föger-Samwald U, Dovjak P, Azizi-Semrad U, Kerschan-Schindl K, Pietschmann P. Osteoporosis: Pathophysiology and therapeutic options. EXCLI J. 2020 Jul 20;19:1017-1037. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-2591. PMID: 32788914; PMCID: PMC7415937.
- Zhao, N., Zhu, X., Xie, L. et al. The Combination of Citicoline and Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Induces Neurite Outgrowth and Mitigates Vascular Cognitive Impairment via SIRT1/CREB Pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-023-01416-7
- Raj Kafle, S., Kushwaha, A., Goswami, L., Maharjan, A., & Soo Kim, B. (2023). A holistic approach for process intensification of nicotinamide mononucleotide production via high cell density cultivation under exponential feeding strategy. Bioresource Technology, 129911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129911
- Shade, C. (2020). The Science Behind NMN–A Stable, Reliable NAD+Activator and Anti-Aging Molecule. Integrative Medicine: A Clinician’s Journal, 19(1), 12-14. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7238909/
- Tang, Z., Bao, P., Ling, X., Qiu, Z., Zhang, B., & Hao, T. (2023). In vitro digestion under simulated saliva, gastric and small intestinal conditions and fermentation of nicotinamide mononucleotide, and its effects on the gut microbiota. Food Research International, 113779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113779
- Tao Li, Yanxiao Li, Qiaojuan Yan, Zhengqiang Jiang, Shaoqing Yang, Co-treatment of nicotinamide mononucleotide and neoagarooligosaccharide mitigates aging-induced cognitive impairment by promoting mitochondrial dynamics, Journal of Functional Foods, Volume 112, 2024, 105922, ISSN 1756-4646, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2023.105922.

