NMN Significantly Boosts NAD+ Levels and Enhances Physical Function in Latest Human Trial
NMN raises blood NAD+, increases six-minute walking distance, and improves self-evaluation of overall health, especially at higher doses in middle-aged, healthy adults.
Highlights
- Taking NMN at doses of 300 mg, 600 mg, or 900 mg per day for 60 days significantly increases blood levels of the pro-longevity molecule NAD+.
- Taking these NMN doses for 60 days substantially increases the distance walked over a six-minute period, an indicator of improved physical function.
- An evaluation measuring perceptions of health and wellbeing indicates improvement in how those who take NMN feel.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a precursor to the cell-health-promoting molecule nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). Rodent studies have shown that supplementing with NMN increases blood NAD+ levels, improves running endurance, and enhances cardiovascular health. Yet whether these findings translate to humans has had mixed results from clinical trials. Some clinical studies suggest that NMN may increase blood NAD+ levels, while others show negative results. In a similar regard, some clinical trials have shown NMN improves muscle function, while others have shown mixed findings related to improved muscle function.
Published in GeroScience, Yi and colleagues from Abinopharm in Connecticut show that supplementing with NMN significantly increases blood NAD+ levels. Moreover, NMN improves physical function as measured by the distance participants walk over a six-minute period. An evaluation of perceptions of health and wellbeing also demonstrated that individuals who took NMN feel better after 30 and 60 days of taking the compound. These findings support that NMN increases blood NAD+ levels, improves physical function, and stimulates perceptions of health and wellbeing.
NMN Increases Blood NAD+ and Improves Muscle Function and Perceptions of Health
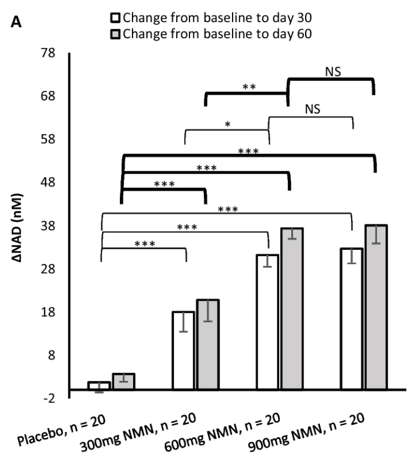
To find whether NMN increases blood NAD+ and whether dosage has an effect, Yi and colleagues measured the blood NAD+ concentration in response to 300, 600, or 900 mg of NMN in middle-aged adults. The Abinopharm-based team found that all doses drove higher blood NAD+ levels measured at day 30 and day 60 of supplementation. The 600 mg and 900 mg per day doses stimulated higher blood NAD+ levels than the 300 mg per day dose. These results suggest that while 300 mg of NMN per day drives much higher blood NAD+ levels than no NMN, taking at least 600 mg per day can be used to maximize blood NAD+ levels.
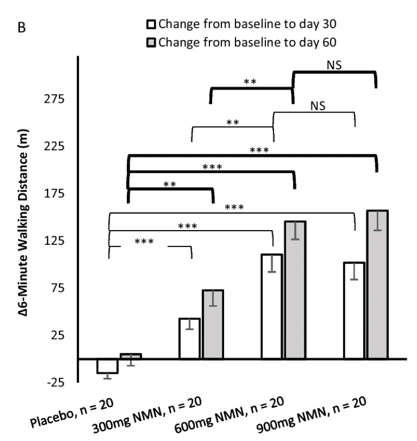
To find whether increased blood NAD+ levels are associated with improved muscle function, Yi and colleagues measured the distances walked by participants over a six-minute period. They found that all doses resulted in longer distances walked at days 30 and 60 of taking NMN, but the 600 mg and 900 mg per day dosing groups walked longer distances than the 300 mg per day group. Since walking distance for six minutes is an indicator of muscle function, these findings suggest that taking NMN at doses of at least 600 mg per day can enhance muscle endurance.
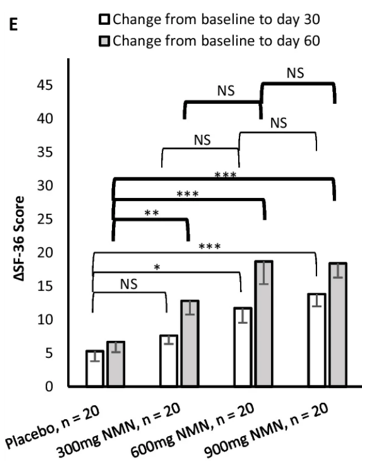
Yi and colleagues had all participants evaluate their perceptions of overall health and wellbeing before and after taking NMN. This assessment tallied answers to a questionnaire (the SF-36) asking about parameters related to self-perceived mental and physical function. The evaluation scores suggested that the 300 mg per day dose improved overall health and wellbeing after 60 days but not 30 days. The 600 mg and 900 mg per day doses improved perceptions of health and wellbeing after both 30 and 60 days. These findings suggest that while 300 mg per day doses can improve perceptions of health and wellbeing after 60 days, doses of at least 600 mg per day may confer these benefits 30 days earlier.
The study provides data supporting that NMN increases blood NAD+ levels and improves muscle function. As this study had only 20 participants per group, more subjects for the study and a longer testing duration would enhance the meaningfulness of these findings. Moreover, looking at other parameters like muscle force would show whether NMN improves strength in addition to endurance.
Ongoing Clinical Trials to Reveal NMN’s Health Benefits
Other clinical trials are in the works that will examine more about NMN’s effects on more specific age-related conditions like high blood pressure, metabolic disorders, and skin aging. Another clinical trial pertaining to muscle recovery following exercise is underway, which may provide tell-tale data about whether NMN helps with muscle function. Adding more clinical data to Yi and colleagues’ findings in the next year or two should reveal whether NMN’s pro-longevity hype is warranted.
Model: Healthy humans aged 40 to 65 years
Dosage: 300 mg, 600 mg, or 900 mg of NMN per day for 60 days

