Crucial Element of Young Blood That Extends Life Discovered
Scientists moderately prolong the lifespan of aged mice with nanosized messengers called extracellular vesicles from young mouse blood.
Highlights:
- Young extracellular vesicles (EVs) prolong the lifespan of older mice by 12.42%.
- Molecules called microRNAs within the EVs improve mitochondrial health.
- EV therapy may be a thing of the future, but supplements like NMN can also improve mitochondrial health.
In the past few decades, scientists have discovered nanosized messengers in our blood that spread information to our cells. These messengers called extracellular vesicles (EVs), may mediate the aging process by exerting holistic effects on the body.
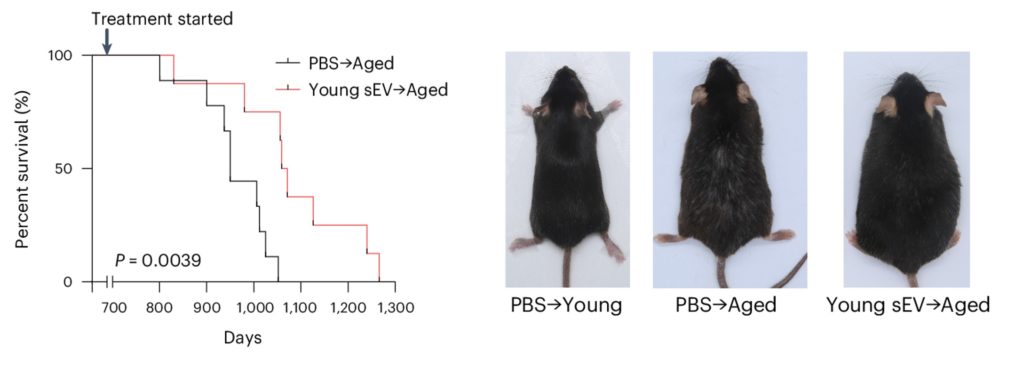
As reported in Nature Aging, older mice injected with EVs from young mice live 12.42% longer. In humans, this is roughly equivalent to living 8 extra years. Not only this but in addition to living longer, the older mice showed no sign of hair loss or graying. Furthermore, they had the memory and endurance of much younger mice. All told, these findings suggest that young EVs can potentially reverse the consequences of aging.
“Blood-borne EVs carry a payload of information that exerts a comprehensive and profound influence on systemic communication. In fact, previous studies provided substantial circumstantial evidence supporting the critical functions of EVs in aging,” said the authors.
EVs are membrane-bound sacs secreted by cells that carry various molecules to other cells. In searching for how young EVs could be exerting their age-reversal effects, researchers found that young EVs carry molecules called microRNAs — short strands of RNA that modulate the activation of genes. These microRNAs were found to recapitulate some of the effects of young EVs.
More specifically, the microRNAs from young EVs improved mitochondrial health. Mitochondria are responsible for generating the majority of our cells’ energy, but with age, mitochondria deteriorate and produce less energy. Inevitably, a lack of energy triggers the degeneration of organs and tissues — what we call aging. It follows that improving mitochondrial health could prevent or slow aging by restoring our cells’ energy levels.
Still, the authors of the study point out that EVs carry a multitude of molecules, including different species of microRNAs, proteins, lipids, and DNAs. Each of these molecules could contribute to reversing aging in different ways. For example, a previous study showed that NAMPT enzymes from young EVs, which help with boosting NAD+, prolong the lifespan of mice. With this in mind, scientists will need to determine how the full repertoire of molecules in young EVs could reverse aging.
Young EV Age-Reversal Therapy
Previous studies have shown that joining the circulatory systems of young and old mice reverses the aging of older mice. Since then, several age-reversing molecules from young blood have been discovered. Moreover, young blood, specifically young plasma, injections have been tested on Alzheimer’s patients. However, while the treatment was safe, it did not significantly improve the cognition of the patients.
Furthermore, young blood or plasma infusions can potentially cause problems like allergic reactions and the transmission of infectious disease. There may also be difficulties in finding suitable quantities of young blood donors to treat the world’s rising population of older individuals. In contrast, young EVs can be harvested from cells grown in a lab and are more biocompatible with most individuals.
Clinical trials utilizing EVs are now underway with most testing the effects of EVs against COVID-19. Considering their acceptance as a viable therapy in these studies, it may not be long before we see young EVs being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of age-related diseases like Alzheimer’s.

